The Galilean Moons of Jupiter: A Detailed Exploration
In 1610, the renowned Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei made a groundbreaking discovery when he identified four of Jupiter’s largest moons: Ganymede, Callisto, Europa, and Io. These moons, commonly referred to as the Galilean moons, have captured the fascination of scientists and space enthusiasts for centuries.
Over the past 400 years, advancements in telescope technology and the advent of space exploration missions have provided us with unprecedented insights into these celestial bodies. Notably, NASA’s Juno spacecraft has played a pivotal role in expanding our understanding of Jupiter and its moons through close flybys and high-resolution imagery.
The Fascinating World of Io
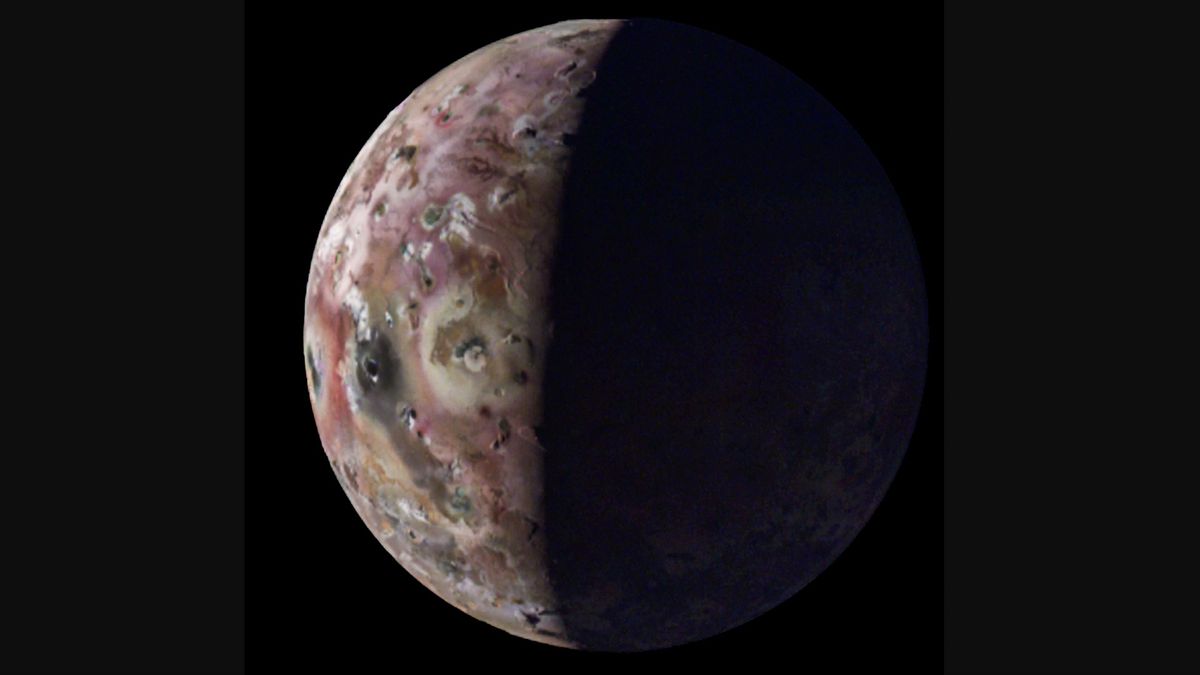
Among the Galilean moons, Io stands out as the most volcanically active body in our solar system. Recent flybys conducted by Juno have revealed a landscape dotted with numerous active volcanoes, offering scientists a glimpse into the dynamic geology of the moon.
During these close encounters, Juno captured stunning imagery of a massive lava lake known as Loki Patera, measuring approximately 200 kilometers in length. The intricate details observed on Io’s surface, including glass-like smooth areas and molten lava flows, have provided valuable insights into the moon’s complex volcanic processes.
The data collected by Juno’s instruments during these flybys have allowed researchers to create captivating animations that showcase the rugged terrain and geological features of Io in unprecedented detail.
Exploring Jupiter’s Poles
In addition to studying Jupiter’s moons, Juno has also focused on unraveling the mysteries of the gas giant itself. By utilizing its Microwave Radiometer instrument, Juno has investigated the unique atmospheric dynamics of Jupiter, including its polar cyclones.
One of the most intriguing discoveries made by Juno’s team is the disparity in the microwave signatures of Jupiter’s north polar cyclones. Through infrared and visible light imaging, researchers have observed distinct differences in the structure and behavior of these enigmatic storms, providing valuable insights into Jupiter’s atmospheric composition.
Moreover, Juno’s observations have shed light on the water abundance near Jupiter’s equator, revealing an intriguing disparity compared to solar levels. These findings not only enhance our understanding of Jupiter’s formation but also offer key insights into the dynamics of gas giant planets.
Continued Scientific Endeavors
As Juno embarks on its extended mission, scientists remain dedicated to uncovering further mysteries surrounding Jupiter and its moons. With upcoming close flybys and innovative data analysis techniques, the Juno team is poised to revolutionize our knowledge of the largest planet in the solar system.
Through ongoing research and exploration, the legacy of Galileo’s discoveries lives on, inspiring generations of astronomers and space enthusiasts to delve deeper into the captivating realm of the Galilean moons and their enigmatic host planet, Jupiter.
Image/Photo credit: source url