Nova Outburst Forecasted to Enliven Night Sky with Spectacular Display
A rare celestial event is on the horizon, promising to illuminate the night sky with a brilliant nova outburst, visible to the naked eye. The phenomenon is set to be orchestrated by the star system T Coronae Borealis (T CrB), situated a staggering 3,000 light-years away from our planet. Comprised of a red giant star and a white dwarf in a harmonious orbital dance, this cosmic pair is poised to captivate observers with a mesmerizing display of stellar fireworks.
Unveiling the Mechanics Behind the Nova Outburst
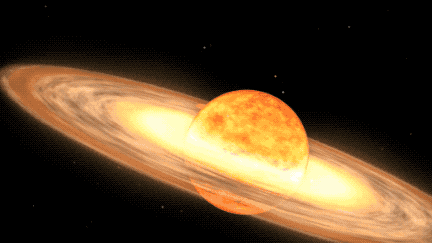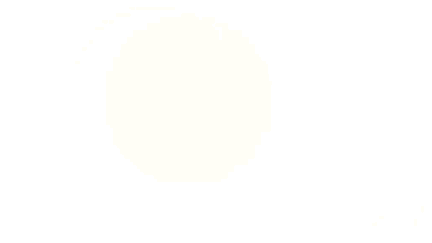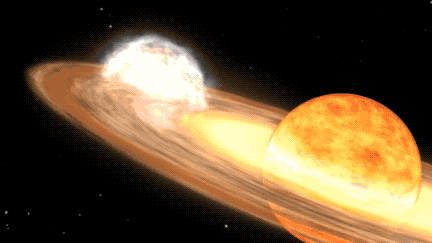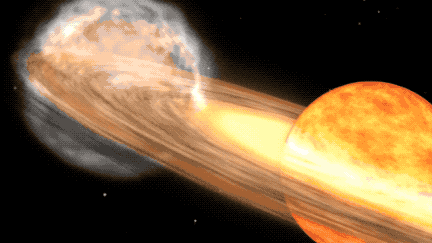
When the white dwarf of the T CrB system siphons off substantial material from its red giant companion, a striking burst of nuclear fusion ensues on the surface of the former, triggering the celestial spectacle known as a nova outburst. This extraordinary astronomical event will grace the constellation Corona Borealis, commonly referred to as the Northern Crown, which encompasses a semicircle of shimmering stars. NASA experts anticipate that the outburst will manifest between the months of February and September in 2024, radiating with a luminosity akin to the North Star before gradually waning.
Unprecedented Observational Opportunity
Characterizing it as a potentially once-in-a-lifetime observance, NASA officials underscore the infrequency of nova outbursts, which materialize only approximately every 80 years. This episodic recurrence marks T CrB as one of merely five such phenomena documented within the Milky Way galaxy. To catch a glimpse of this celestial extravaganza, stargazers are encouraged to direct their gaze towards Corona Borealis, nestled between the constellations Boötes and Hercules. The outburst will manifest as a radiant “new” star in the nocturnal firmament.
Ordinarily obscured by its faint magnitude of +10, this binary star system will emerge in full splendor during the outburst, boasting a magnitude comparable to that of the North Star, Polaris. Following its zenith, the nova will remain perceptible to the unaided eye for several days and extend its luminosity to roughly a week when observed through binoculars, before gradually receding into obscurity, possibly for the next eight decades.
Understanding the Cosmic Dynamics at Play
The celestial duo comprising the T CrB system constitutes a white dwarf—a diminutive, dense remnant star—alongside a bloated red giant star in the twilight of its stellar evolution. As the red giant’s instability escalates due to mounting temperatures and pressures, it sheds its outer layers onto the white dwarf, setting the stage for the ensuing outburst. The accumulation of matter ignites a thermonuclear reaction within the white dwarf’s atmosphere, epitomizing the breathtaking nova display observed from Earth. This cyclical process of accretion and ignition heralds the promise of subsequent outbursts as the white dwarf replenishes its stellar fuel reserves, perpetuating the cosmic dance of stellar rejuvenation.
Image/Photo credit: source url