Spectacular New Images of Star-Birthing Region in the Triangulum Galaxy
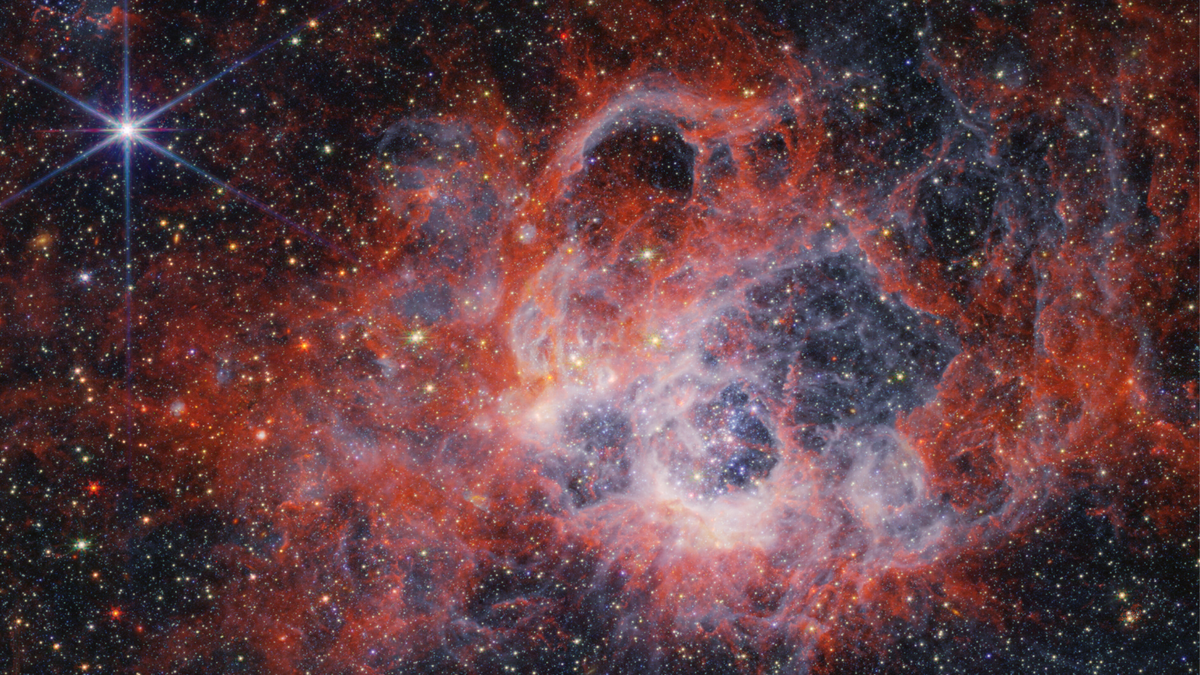
The James Webb Space Telescope has captured two stunning images showcasing the intricate details of a star-forming region in the Triangulum Galaxy. One of these images focuses on NGC 604, a star-birthing area located approximately 2.7 million light-years from Earth within the Triangulum Galaxy, also known as Messier 33 (M33).
The gas clouds present in NGC 604 cover an estimated area of 1,300 light-years. Despite its vastness, NGC 604 is considered young at only 3.5 million years old, making it significantly younger than our solar system at 4.6 billion years old.
Detailed Descriptions of the JWST Images
The images captured by the James Webb Space Telescope reveal the presence of over 200 stars in their early developmental stages within NGC 604. These stars, classified as B- and O-types with mass up to 100 times that of the sun, emit strong radiation and powerful stellar winds that mold the surrounding gas clouds.
Specifically, the NIRCam image illustrates tendrils of gas enveloping the stars, emitting a bright red hue with blue and white glows resulting from ionization of hydrogen gas by ultraviolet light. The orange streaks seen in the NIRCam image represent polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), essential components for star and planet formation, and believed to play a crucial role in the emergence of life on Earth.
Deeper red clouds visible in the NIRCam image indicate un-ionized molecular hydrogen, providing a favorable environment for star formation. Additionally, blue stars can be observed in the process of creating voids within these gas clouds.
On the other hand, the MIRI image captured by the James Webb Space Telescope offers a different perspective of NGC 604. While it lacks the presence of young blue stars seen in the NIRCam image, the MIRI image reveals the glow of red supergiant stars, characterized by their expanded state and cooling temperatures after depleting their hydrogen fuel.
The MIRI image also showcases galaxies located beyond NGC 604, adding to the celestial panorama captured by the telescope. Notably, the blue gas tendrils depicted in the MIRI image emphasize the significant contribution of PAHs to the formation of gas and dust clouds within the M33 star-forming region.
Image/Photo credit: source url