Observing the Moon’s Shadow During a Solar Eclipse
An observer located near or within the path of totality during a solar eclipse has the unique opportunity to witness and make valuable observations of the moon’s shadow as it interacts with the Earth’s atmosphere. These observations, both before and after mid-eclipse, can provide critical insights into the behavior of the shadow and the changing qualities of the sky darkness.
The Ever-Changing Appearance of the Shadow
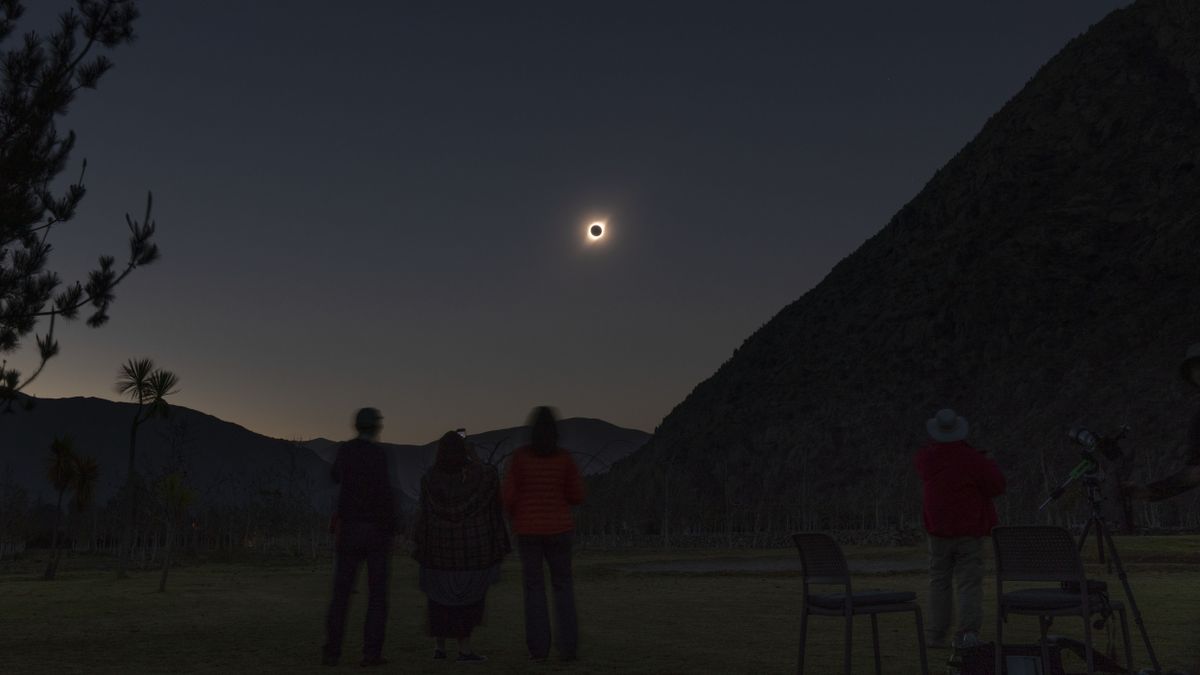
During a total solar eclipse, the moon’s shadow forms an ellipse as it intersects the Earth’s surface, with its major axis pointing towards the direction of the sun. Given the rapid movement of the shadow, its appearance undergoes continuous transformations. Descriptions of the sky’s characteristics during the moments near totality are particularly intriguing, especially observations of the moon’s shadow against the sky as it approaches and recedes surrounding the total eclipse.
Anticipation of the Upcoming Eclipse
Prior to the commencement of totality, a distinctive shadow resembling an approaching storm is expected to become visible in the west-southwest sky, advancing towards the observer. This visual phenomenon serves as a precursor to the main event, signifying the impending arrival of the total solar eclipse.
Experiencing Exotic Colors and Lighting During Totality
The allure of witnessing a total solar eclipse has long been described as a compelling and transformative experience. Individuals, when exposed to the complete immersion of totality, often find themselves in a realm of exotic colors and unusual lighting that defies conventional description.
Astronomy enthusiasts frequently extol the virtues of personally encountering a total solar eclipse to truly grasp the essence of its splendor. The distinct visual ambiance created during totality, marked by ethereal hues and atmospheric phenomena, remains unmatched in its mesmerizing beauty.
A Glimpse of Celestial Objects During Totality
As the sun is obscured during totality, the sky does not plunge into complete darkness akin to a moonlit night. Instead, the illumination level mirrors the pre-dawn or post-sunset period, unveiling celestial objects such as Venus, Jupiter, and prominent stars in the surrounding sky.
Each planet and star plays a role in enhancing the cosmic spectacle, offering spectators a chance to marvel at the intricacies of the celestial realm amidst the backdrop of a total solar eclipse.
Maximizing the Totality Experience
While the temptation to search for stars and planets during totality may be strong, focusing on beholding the solar corona and immersing oneself in the unique ambiance of the eclipse often proves to be a more rewarding endeavor.
By heeding the advice to simply gaze at the event unfolding before you and fully appreciate its grandeur, observers can cultivate a profound sense of awe and wonder during the fleeting moments of totality.
Ensuring Safe Viewing Practices
To ensure a safe viewing experience of the total solar eclipse, it is imperative to utilize solar filters for direct observation of the sun’s corona. Only individuals situated within the path of totality may briefly remove their filters to view the corona with the naked eye.
For those witnessing the partial phases of the eclipse or located outside the path of totality, the use of solar eclipse glasses or protective filters for cameras, telescopes, and binoculars is mandatory throughout the event to safeguard their eyes and equipment.
Additional Resources
For comprehensive guidelines on safe solar observations and detailed instructions on how to observe the sun securely, refer to our comprehensive “How to Observe the Sun Safely” guide. Stay informed about the latest space news, rocket launches, and upcoming skywatching events to enhance your astronomical pursuits.
Image/Photo credit: source url