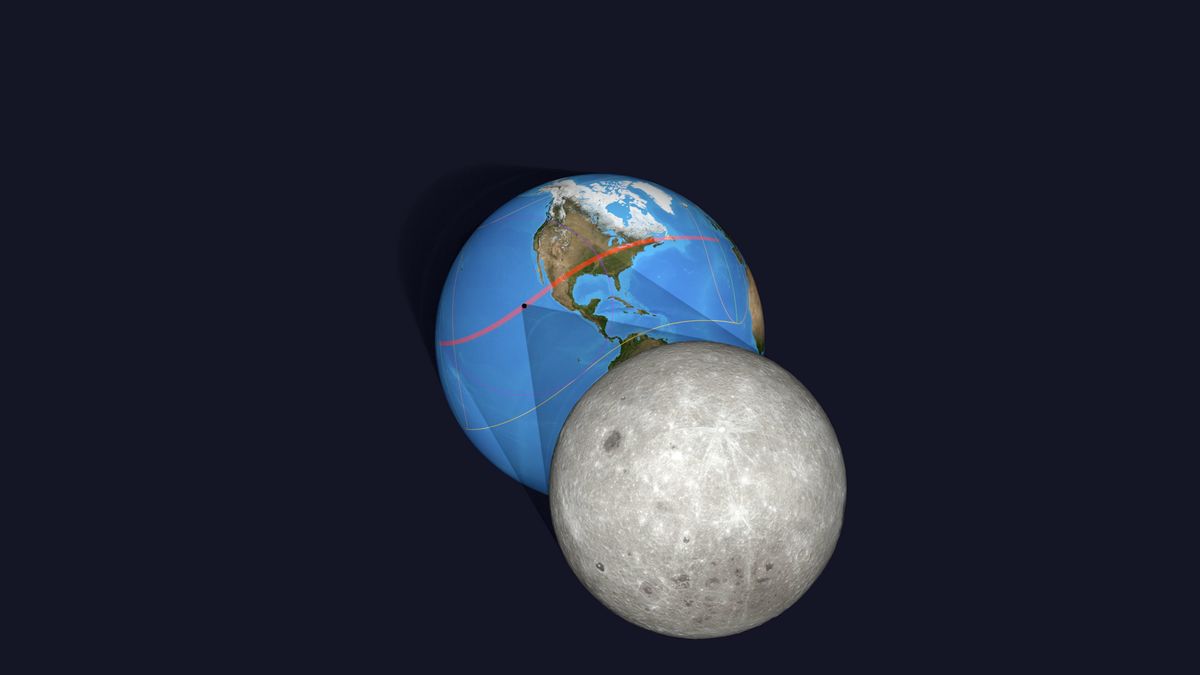
On Monday, March 25th, the upcoming “Worm Moon” will bring about a penumbral lunar eclipse, visible from the night side of Earth across various regions including North and South America, Europe, East Asia, Australia, and New Zealand.
The “Worm Moon,” denoting the third full moon of 2024 and the first of spring in the northern hemisphere, will traverse through Earth’s outer shadow in space, setting the stage for a total solar eclipse precisely two weeks later that will be observable across North America.
The Commencement of 2024’s Prime “Eclipse Season”
During an eclipse season, characterized by a duration of approximately between 31 to 37 days, the moon periodically intersects or almost intersects the ecliptic, the sun’s apparent path through the sky. This alignment occurs due to the moon’s orbit around Earth coinciding with the plane of Earth’s orbit around the sun. Consequently, this period allows for the occurrence of two, and at times three, solar and lunar eclipses within this limited timeframe.
Insight into 2024’s Eclipse Seasons
2024 will feature two eclipse seasons, each hosting two solar eclipses and two lunar eclipses as follows:
Eclipse Season 1
- March 25: a penumbral lunar eclipse of the “Worm Moon” visible in North and South America, Europe, East Asia, Australia, and New Zealand.
- April 8: a total solar eclipse viewable in parts of Mexico, the U.S., and Canada.
Eclipse Season 2
- September 18: a partial lunar eclipse of the “Harvest Moon” observable in Europe, Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Ocean, Arctic, and Antarctica.
- October 2: an annular solar eclipse visible from Easter Island, Rapa Nui, Chile, and Argentina.
While there is no third eclipse scheduled for 2024’s second eclipse season, a near-miss occurs on October 17th, noted by timeanddate as an “almost lunar eclipse.” This occurrence serves to illustrate the mechanism of eclipse seasons, elucidating how the moon narrowly avoids passing through Earth’s shadow. This phenomenon transpires due to the moon’s position at its ascending node the day before, regulating its orbital trajectory.
Understanding the Moon’s Orbital Nodes
The moon’s orbit around Earth is tilted by 5 degrees relative to the ecliptic, ensuring that solar and lunar eclipses do not transpire every month. Eclipses are contingent upon the moon reaching its new or full phase while traversing the ecliptic, known respectively as the ascending and descending nodes. Eclipse seasons are instrumental in aligning the moon with these nodes at the precise moment, fostering the occurrence of solar and lunar eclipses within a condensed timeframe.
Partial and Penumbral Eclipses Unveiled
Partial solar or lunar eclipses, along with penumbral lunar eclipses, materialize during eclipse seasons when the moon marginally deviates from its target trajectory, leading to incomplete eclipses. To experience a total solar or lunar eclipse, the moon must hit the node precisely on time, ensuring either the complete obscuration of the sun or entry into Earth’s shadow.
Conclusively, the pending celestial events offer a rare opportunity to witness the magnificence of astronomical phenomena firsthand, emphasizing the importance of exercising caution and employing proper eye protection when observing solar eclipses to safeguard one’s vision.
Image/Photo credit: source url