Unveiling a New Space Molecule in the Depths of the Cat’s Paw Nebula
Exploration and discovery are at the core of scientific endeavors, propelling us into the vast unknown of the cosmos. In a recent breakthrough, a team of researchers led by Zachary Fried, a graduate student at the prestigious Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), uncovered a groundbreaking revelation while investigating a region teeming with stellar birth, nestled approximately 5,550 light-years away within the Cat’s Paw Nebula, known scientifically as NGC 6334.
Unraveling the Mystery of 2-Methoxyethanol
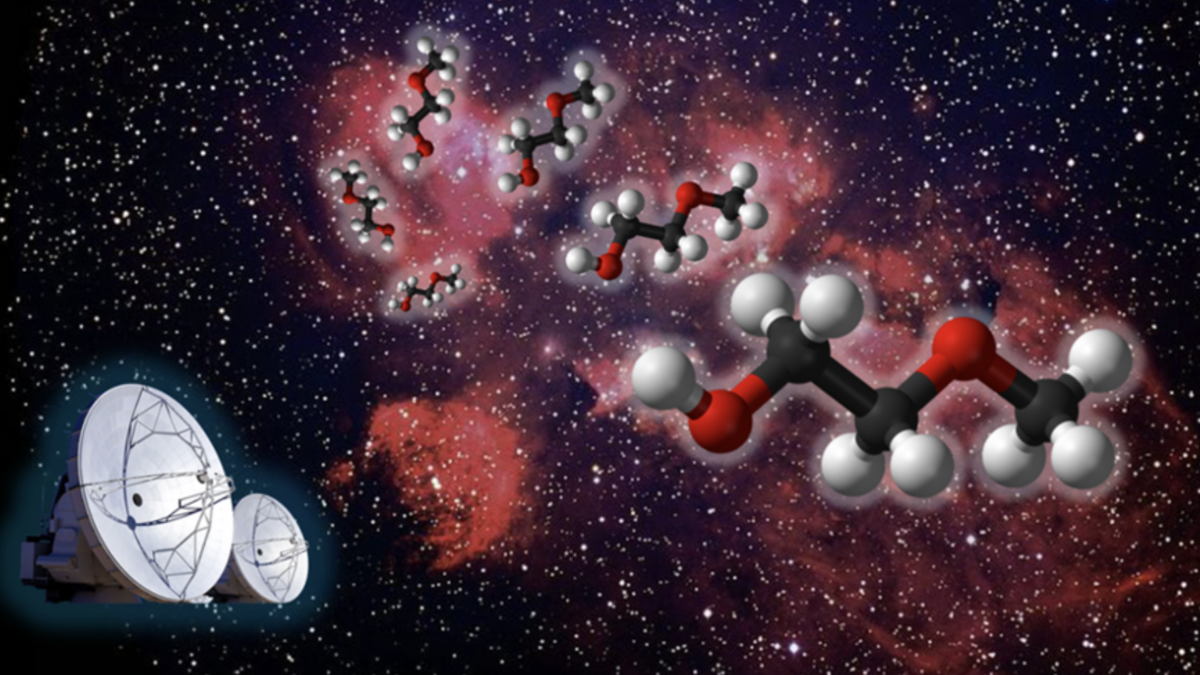
The focal point of this discovery revolves around the identification of a previously undiscovered space molecule, 2-methoxyethanol, within a specific area of the nebula denoted as NGC 6334I. This intricate molecule, comprising a total of 13 atoms, stands out significantly in the realm of cosmic chemistry, marking it as the largest and most intricate “methoxy” compound detected in space thus far.
The significance of this finding lies not only in the novelty of the molecule but also in the insights it offers into the evolutionary processes that govern the formation of stars and planetary systems. As Fried elaborates, “Our group endeavors to elucidate the molecular compositions present in regions where stars and solar systems are poised to emerge, aiding in our comprehension of the intertwined evolution of chemistry alongside stellar and planetary genesis.”
Probing the Depths of Space with ALMA
To conduct this pioneering research, Fried and his team deployed the sophisticated Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), a network of 66 radio telescopes ensconced in the arid expanse of Northern Chile’s Atacama desert. Armed with machine-learning algorithms that guided their pursuit of 2-methoxyethanol, the researchers meticulously analyzed the rotational spectrum of the molecule to establish a distinct blueprint for its detection.
By meticulously scrutinizing the unique patterns of light emissions emitted by 2-methoxyethanol as it tumbles through space, the team successfully confirmed its presence in NGC 6334I. This achievement not only allowed the researchers to determine the molecule’s abundances and excitation temperature within the nebula but also paved the way for probing the potential chemical pathways responsible for its formation.
Implications and Future Prospects
The unveiling of 2-methoxyethanol in the cosmic expanse of NGC 6334I heralds a watershed moment in our understanding of the chemical complexity inherent in stellar nurseries. Through continued observations and analyses of such intricate molecules, scientists can unravel the intricate mechanisms that govern the emergence of larger molecular structures during the cosmic ballet of star and planet formation.
As Fried aptly concludes, “This groundbreaking discovery not only expands our knowledge of large molecule formation in cosmic environments but also presents a unique opportunity to dissect how varying physical conditions shape the chemical landscape across diverse stellar birth sites.”
Published in the esteemed journal The Astrophysical Journal Letters, this seminal research marks a significant leap forward in our quest to comprehend the cosmic tapestry of molecular evolution.
Image/Photo credit: source url