Analysis of US Carbon Emission Trends
Recently, the US Department of Energy disclosed its preliminary report on the nation’s carbon emissions in the preceding year. A decrease in emissions signifies a positive trajectory, potentially averting the catastrophic warming scenarios looming earlier. However, significant reductions are imperative to align with the Paris Agreement’s target of limiting global warming below 2° C.
US Carbon Emission Trajectory
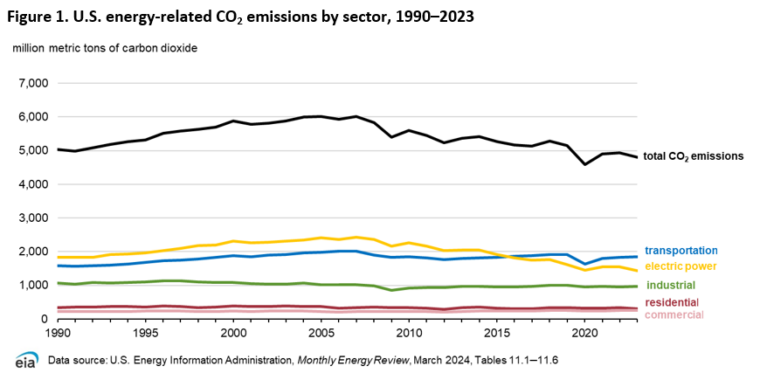
A gradual decline in US carbon emissions has been observed since approximately 2007, following a peak around six gigatonnes. The tumultuous events of 2020, primarily the pandemic, led to a substantial reduction, marking the first instance since pre-1990 figures that emissions fell below five gigatonnes. Despite a slight rise post-pandemic, 2023 witnessed emissions dropping below the five gigatonnes threshold once more.
Impact of the Power Grid
The US Energy Information Agency (EIA) dissects carbon dioxide sources into five sectors, with electricity generation commanding the spotlight. Notably, 80 percent of the emission reduction in 2023 is attributed to the power grid, which is unwaveringly the sole sector exhibiting notable transformation amidst the EIA’s 30-year observation period.
Historically reliant on coal for over half of its electricity output, the US has now drastically minimized coal’s role to a mere 16 percent, overtaken by the ascension of wind and solar energy. Wind and solar generation, previously negligible before 2004, are poised to surpass coal and nuclear derivatives at a rapid pace.
Despite a decline in wind energy generation in 2023 due to prevailing low wind speeds, renewable sources are gradually overshadowing traditional coal and nuclear power. Notably, natural gas usage in electricity generation has surged from 10 percent in 1990 to over 40 percent in 2023, reshaping the energy landscape.
Challenges and Prospects
While minor reductions in energy consumption have contributed to decreased emissions, upcoming shifts in demand patterns, especially driven by transport and appliance electrification and AI proliferation, foreshadow a surge in electricity needs. Notably, the power grid currently accounts for 30 percent of US emissions, standing as the second-largest contributor, with transportation leading at 39 percent.
Despite continued decarbonization efforts, certain sectors like transportation display stagnant emission levels. Nevertheless, future regulatory measures prioritizing fuel efficiency herald a decline in transportation emissions. Residential, commercial, and industrial sectors also exhibit promising signs, with advancements in energy-efficient technologies influencing emission reductions.
Both optimistic and critical perspectives on the data conclude that while advancements have been made, substantial challenges lie ahead. Accelerating decarbonization efforts and addressing sectors resistant to change remain pivotal. The Biden administration’s initiatives seek to propel progress, but significant impacts may manifest only beyond the current decade.
Image/Photo credit: source url