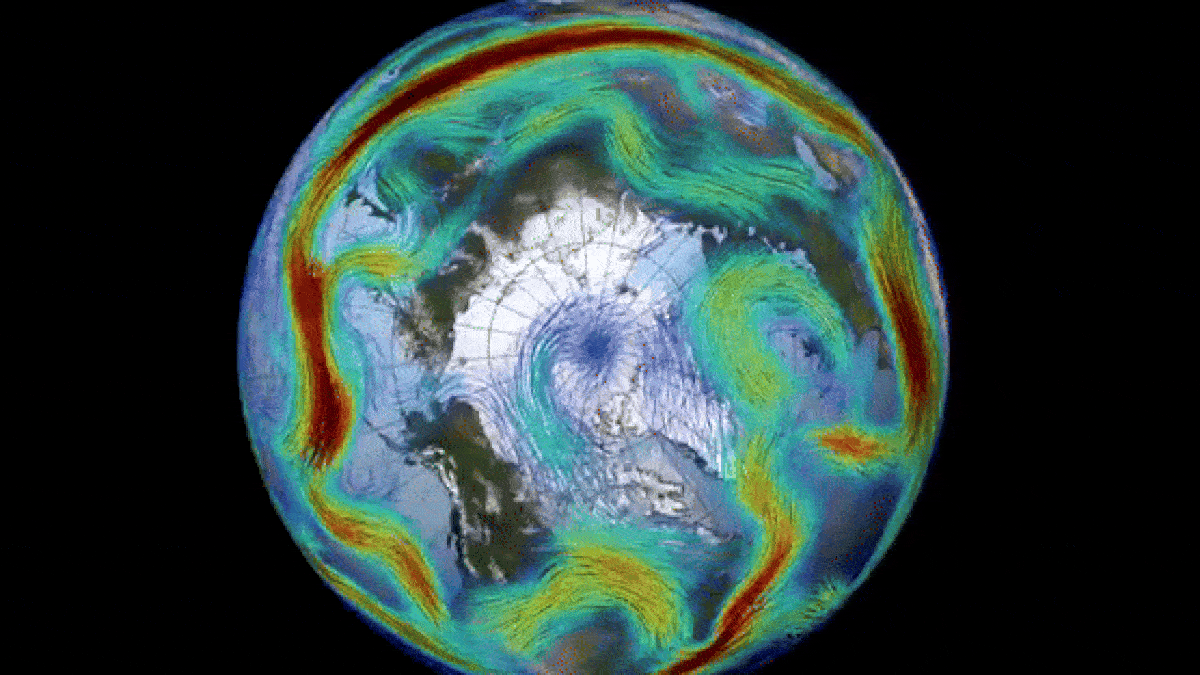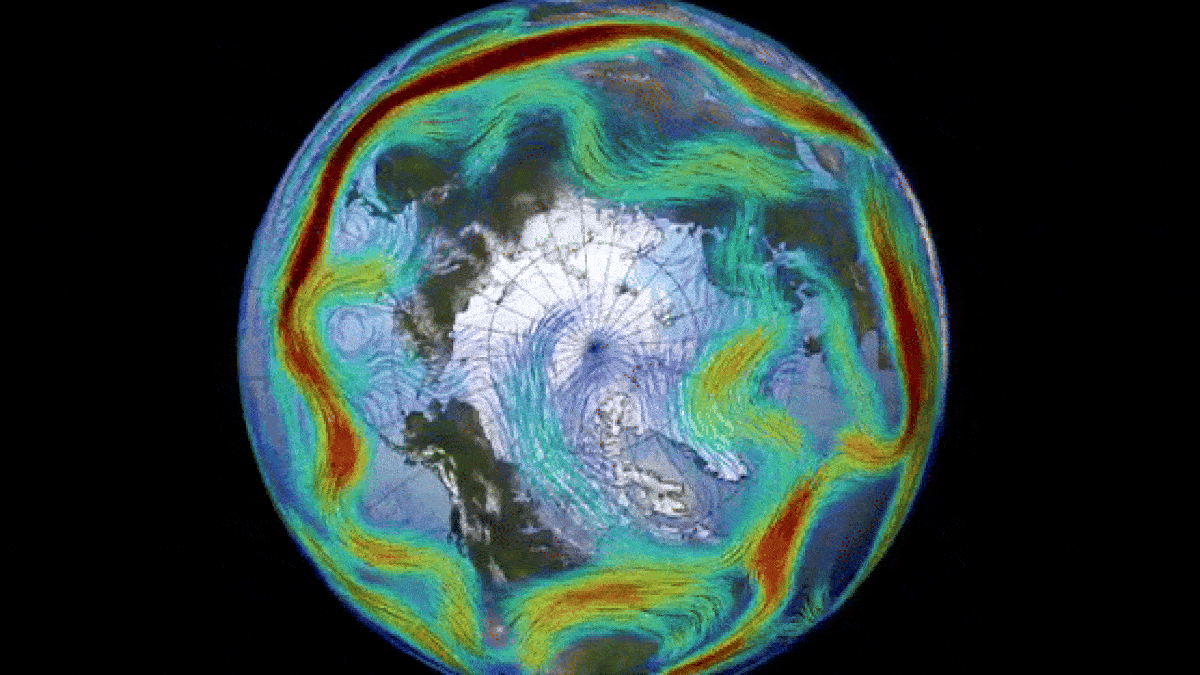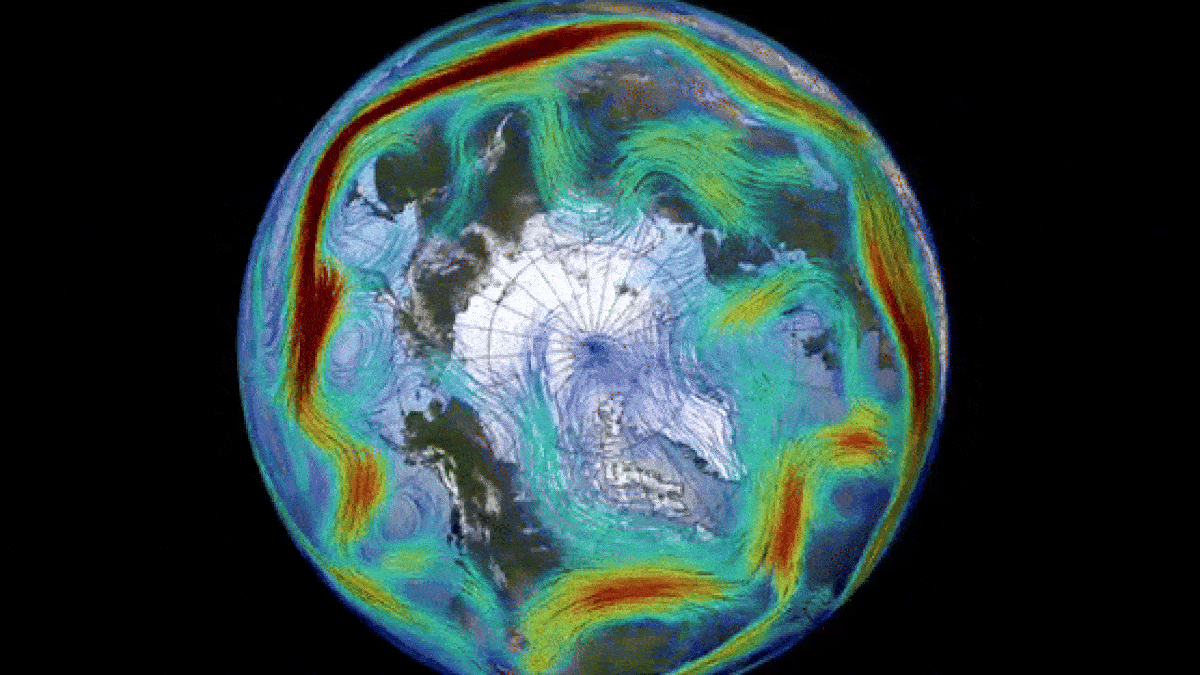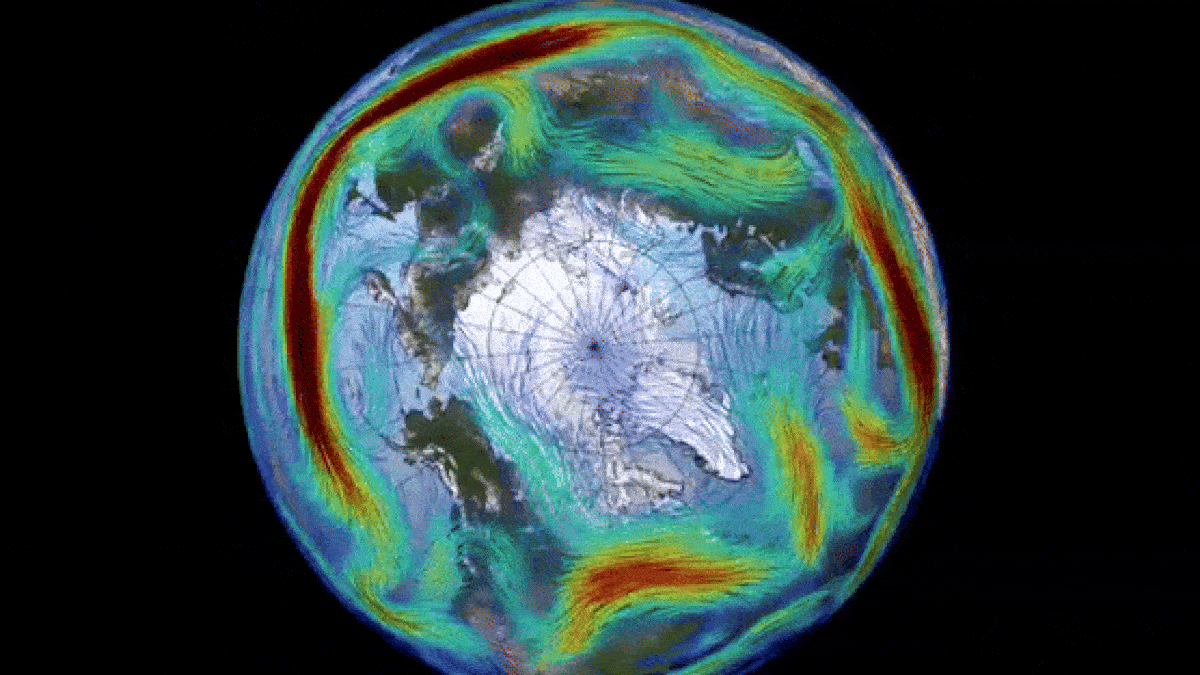
The Arctic’s Unexpected Atmospheric Event
Recent atmospheric observations have unveiled an unusual reversal of the polar vortex encircling the Arctic, sparking interest and concern among climate scientists and meteorologists. The unexpected event occurred as a result of a sudden warming episode in Earth’s atmosphere, leading to one of the most extreme shifts in the vortex’s rotation witnessed in recent history.
The Nature of the Polar Vortex
The polar vortex, a massive circulating system of cold air in the Arctic region, is most noticeable during winter months and extends into the stratosphere, reaching up to 30 miles above the Earth’s surface. With wind speeds comparable to those of a Category 5 hurricane, this weather phenomenon is a critical component of the Earth’s atmospheric dynamics.
During periods of sudden stratospheric warming (SSW), such as the one observed this past March, the polar vortex can undergo temporary reversals. SSW events, characterized by a rapid increase in stratospheric temperatures, disrupt the normal flow of the vortex and create drastic shifts in atmospheric circulation.
Impact on Weather Patterns
While past disruptions to the polar vortex have led to severe cold spells and storms across the United States, the current reversal is unlikely to result in a similar outcome. However, the anomalous atmospheric conditions have resulted in a record-breaking surge of ozone above the North Pole, highlighting the complex interplay of factors influencing Earth’s climate.
Despite the significant nature of the recent vortex reversal, experts anticipate a return to normalcy as the winds begin to show signs of subsiding. Climate scientists like Amy Butler from NOAA have emphasized the importance of monitoring these events closely to better understand their implications on global weather patterns.
Implications of Climate Variability
The occurrence of SSW events like the one witnessed in March is often associated with broader climate phenomena, such as El Niño and La Niña cycles. These natural climate patterns can increase the likelihood of vortex disruptions and reversals, underscoring the intricate relationship between regional weather systems and global climate dynamics.
As we navigate through a significant El Niño phase, scientists remain vigilant in analyzing potential impacts on atmospheric circulation and weather variability. By studying and documenting these events, researchers can enhance our knowledge of Earth’s climate processes and improve our ability to predict future atmospheric disruptions.
Image/Photo credit: source url