Strengthening Space Debris Procedures in China
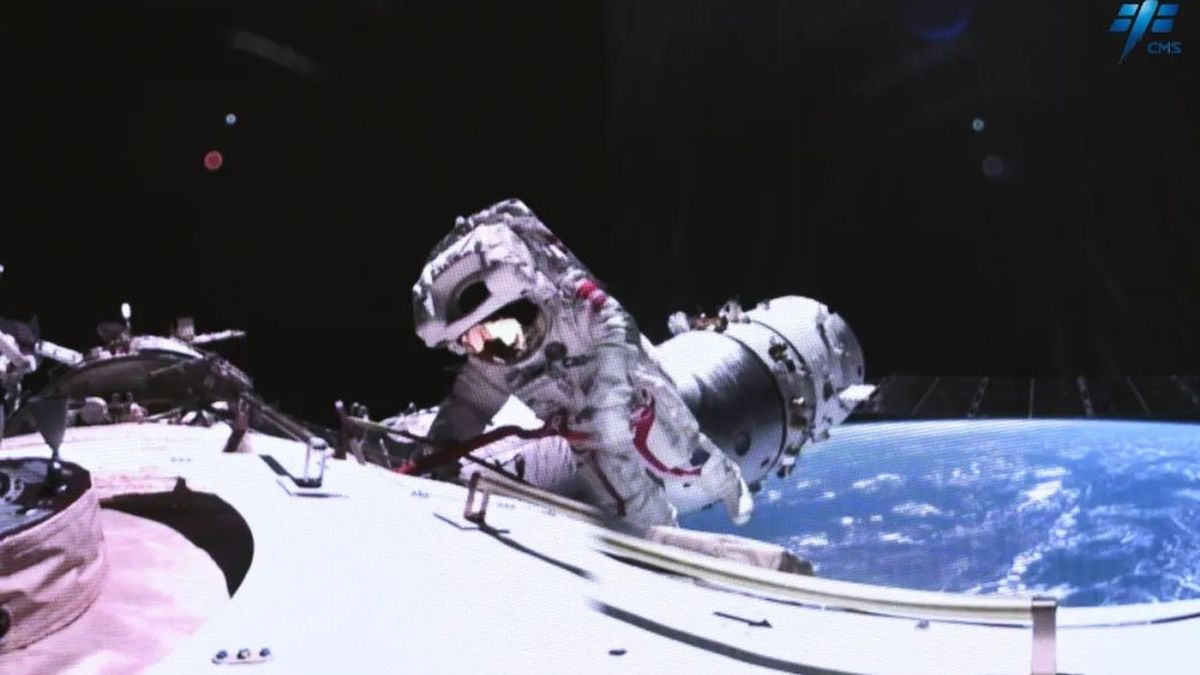
Following a recent incident involving a partial loss of power on China’s Tiangong space station due to a debris strike, Chinese authorities have outlined plans to enhance their space debris mitigation strategies for astronauts. The incident occurred during the Shenzhou 17 mission, where astronauts conducted successful spacewalks despite the minor power supply disruption on March 1.
The China Manned Space Agency (CMSA) confirmed the incident during a press conference reported by Xinhua, the state-run media outlet. CMSA deputy director Lin Xiqiang emphasized the need for increased vigilance against space debris threats in orbit. According to Lin, the Tiangong space station’s core module, Tianhe, experienced a partial loss of power supply following the impact of space debris on the solar wing’s power cables.
The origin of the debris, whether from micrometeoroids or human activities in space, remains unspecified by Xinhua. However, the prevalence of space debris poses a significant risk not only to Tiangong but also to the International Space Station (ISS). Human-generated orbital debris is on the rise, with the North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD) tracking over 43,000 space objects as of April 2024.
Orbital Debris Management
NORAD’s tracking efforts are crucial for safeguarding orbital assets, as evident by the more than 30 instances where ISS controllers had to maneuver the station away from debris since its inception in 1998. Strict guidelines dictate the need for evasive maneuvers when debris encroaches within a defined proximity around the ISS.
Similarly, China has proactively maneuvered the Tiangong space station on multiple occasions to avoid potential collisions with space debris. Lin highlighted various measures undertaken by the CMSA to improve debris forecasting, collision warning procedures, and overall risk mitigation strategies.
Future Initiatives and Collaborations
Looking ahead, China plans to implement additional measures to enhance space debris protection. These include increased video surveillance of Tiangong utilizing a high-definition camera mounted on its robotic arm. Furthermore, the upcoming Shenzhou 18 mission aims to install reinforcements for extravehicular piping, cables, and critical equipment to mitigate debris impact risks.
In contrast to collaborative efforts in lunar exploration, NASA and China operate independently in space activities due to the restrictions imposed by the Wolf amendment. Despite these limitations, both agencies have formed partnerships with other nations to advance their respective space exploration agendas. NASA’s Artemis Accords have garnered support from nearly 40 countries, while China, in collaboration with Russia, has welcomed new partners like Nicaragua, the Asia-Pacific Space Cooperation Organization, and the Arab Union for Astronomy and Space Science.
Image/Photo credit: source url