Optimizing 5G Tower Densification for Improved Battery Life
Recent research conducted by experts from the University of California San Diego proposes a groundbreaking solution to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of urban 5G networks. The study suggests that deploying numerous smaller 5G towers, as opposed to traditional large towers, could extend the battery life of smartphones by up to 50% across urban areas. This innovative approach not only benefits individual users but also has substantial environmental advantages, as highlighted in a report featured in New Scientist.
Key Findings of the Study
The researchers at UC San Diego emphasize that a strategy focused on densifying 5G tower placement offers a dual-pronged solution to prevalent challenges. By avoiding the substantial energy losses associated with high-range signal transmission, the proposed network configuration could potentially achieve triple the power savings. Moreover, smartphones connected to these compact towers stand to benefit from a significant improvement in battery performance due to their proximity and reduced signal interference.
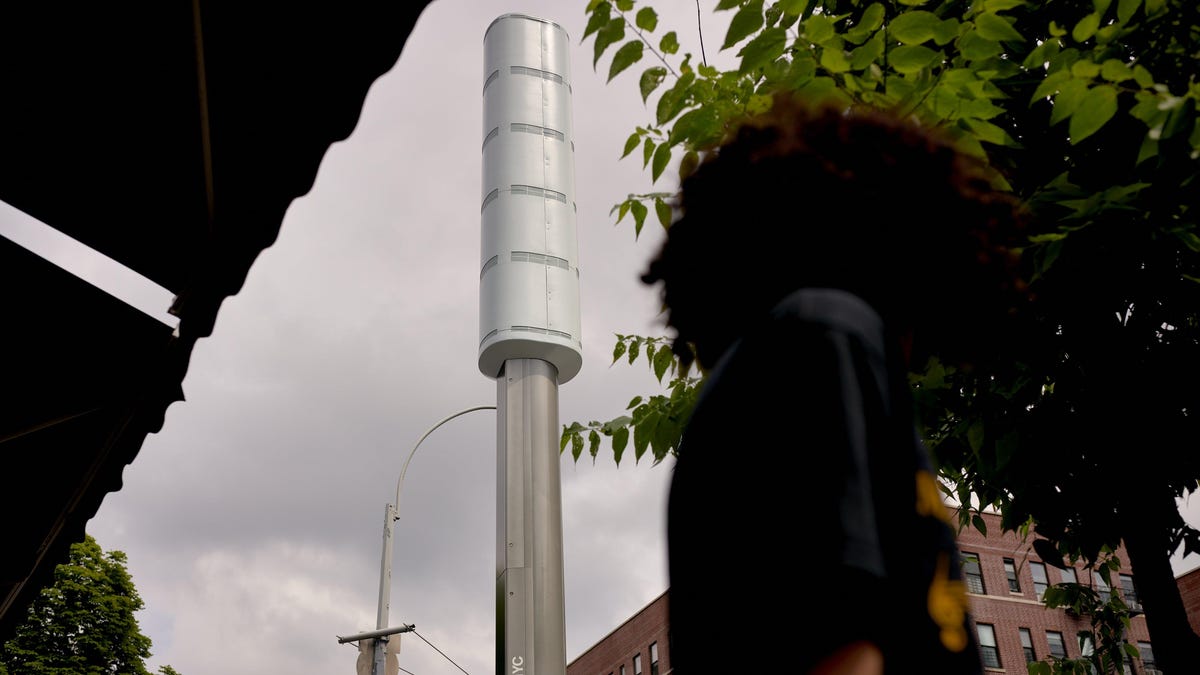
Titled “Densify & Conquer,” the academic paper underscores the necessity for urban regions to transition from conventional large-power base stations to small-cell networks. Rather than relying on a single expansive tower with a wide signal coverage, the researchers advocate for employing multiple smaller towers with narrower signal ranges. While each individual tower may have a weaker signal output, the collective network strength and efficiency far exceed that of a singular tower.
Implications for Energy Consumption and Network Coverage
The fundamental premise behind the projected 50% battery life enhancement lies in the quality and strength of cellular signals within a small-cell network. Stronger signals mean reduced data packet transmission requirements, thereby minimizing device strain and optimizing energy consumption. In the grand scheme of urban living, the aggregate effect of superior network connectivity translates to reduced carbon footprints as fewer devices require frequent recharging.
Notably, the viability of this small-cell network concept is largely attributed to the intrinsic capabilities of 5G technology. Unlike previous generations of wireless networks, 5G networks boast seamless tower-to-tower transitions, facilitating the seamless operation of a denser tower network. This technological advancement eliminates latency issues that previously hindered the feasibility of such a configuration, making it a practical and sustainable solution for modern urban environments.
Practical Implementations and Cost-Effectiveness
Through the utilization of open-source software and sophisticated modeling techniques, researchers were able to simulate the performance of small-cell networks in realistic urban environments. Their findings suggest that while a denser tower network may require up to five times more individual towers, each tower’s modest height of 15 meters allows for versatile installation on existing infrastructure such as street lights or buildings. This cost-effective approach presents a win-win scenario for network providers and urban residents by optimizing coverage and reducing energy consumption simultaneously.
In conclusion, the paradigm shift towards small-cell 5G tower densification represents a pivotal moment in the evolution of urban connectivity. By embracing innovation and sustainable practices, cities can unlock unprecedented benefits in terms of energy efficiency, network performance, and overall user experience.
Image/Photo credit: source url